 |
 |
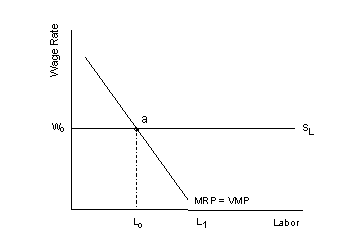
Labor Market Perfectly
Competitive |
Labor Market Perfectly
Competitive |
 |
 |
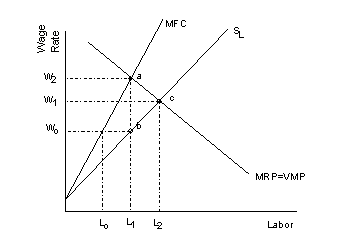
Labor Market Monopsony |
Labor Market Monopsony |
 |
 |
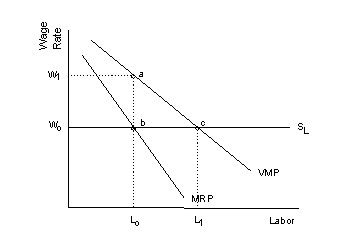
Labor Market Perfectly
Competitive |
Labor Market Perfectly
Competitive |
 |
 |
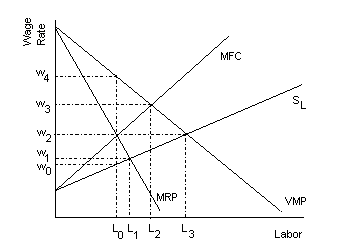
Labor Market Monopsony |
Labor Market Monopsony |