Economics 155 Final Exam
Fall 1998
- 1. Economics is best defined as the study of
- a. how to make money.
- b. how people allocate scarce resources among unlimited
wants.
- c. how prices are determined.
- d. how people attempt to maximize their satisfaction,
given their limited incomes.
- 2. Incorrectly implying cause-and-effect relationship
between two events is a logical fallacy called
- a. fallacy of composition.
- b. normative analysis.
- c. rational self-interest.
- d. post hoc fallacy.
- 3. Opportunity cost is best defined as
- a. the highest valued alternative given up when a choice
is made.
- b. the cost of a good minus profits.
- c. the sum of all alternatives given up when a choice is
made.
- d. the money spent once a choice is made.
- 4. A production possibilities curve is usually shown as
bowed out (concave from the origin) because of
- a. changes in unemployment of resources due to movement
along a production possibilities curve.
- b. recognition that resources are not equally suited for
the production of all goods.
- c. inflation.
- d. the tradeoff involved in all choices/decisions.
- e. the laws of supply and demand.
Use the Following Table to Answer Question
5
- Production Possibilities Schedule
|
- Choice
|
- Capital
|
- Consumption
- Goods
|
- A
|
- 0
|
- 10
|
- B
|
- 1
|
- 9
|
- C
|
- 2
|
- 7
|
- D
|
- 3
|
- 4
|
- E
|
- 4
|
- 0
|
- 5. As compared to the production possibility choice C in
the Production Possibilities Schedule above, the choice
of production possibility D would
- a. cost 3 units of consumption goods.
- b. be unobtainable.
- c. give rise to some unemployment.
- d. be preferred by society.
- 6. A rightward shift of the production possibilities
curve might be caused by
- a. a decrease in technology.
- b. a decrease in the population of the country.
- c. a general increase in worker productivity.
- d. reduction in unemployment.
- 7. According to the law of demand, if the price of CDs
decreased
- a. the quantity demanded of CDs would increase.
- b. the demand for CDs would decrease.
- c. the demand for CDs would increase.
- d. the quantity demanded of CDs would decrease.
- 8. If an increase in the price of product X causes a
decrease in the demand for product Y, we can conclude
that
- a. the price of Y will increase.
- b. the quantity of Y sold will increase.
- c. they are complements.
- d. they are substitutes.
- 9. Last year a firm made 1,000 units of its good
available at a price of $5 per unit. This year the firm
would be willing to make 1,000 units available but only
if the price is $7 per unit. What has most likely
happened?
- a. Demand has decreased.
- b. Demand has increased.
- c. Supply has increased.
- d. Supply has decreased.
- 10. A change in supply cannot be caused by
- a. a change in the price of inputs.
- b. an increase in the number of consumers.
- c. changes in the profitability of producing other
products.
- d. an improvement in technology.
Use the Following Graph to Answer Question
11

- 11. According to the graph above, what price would result
in a surplus of 100 units of this product?
- a. $6
- b. $2
- c. $10
- d. None of the above.
- 12. If price is below equilibrium
- a. quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied, and a
shortage exists.
- b. demand will increase.
- c. demand is too low for equilibrium.
- d. quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded, and a
shortage exists.
- 13. Assume standard supply and demand curves. There is a
simultaneous decrease in demand and decrease in supply.
What will be the effect on equilibrium price and
quantity?
- a. Both price change and quantity change are
indeterminate.
- b. Price change is indeterminate and quantity decreases.
- c. Price is stable and quantity decreases.
- d. Price decreases and quantity change is indeterminate.
- e. Price change is indeterminate and quantity is stable.
- 14. The distinguishing characteristic of a "public
good" is that
- a. only government employees benefit from the good, even
though all taxpayers must help pay for it.
- b. it exhibits the non-exclusion principle.
- c. it is divisible.
- d. it will not be produced by the private market since no
one wants it.
- 15. A tax which takes a greater percent of income as
income increases is called
- a. regressive.
- b. poll tax.
- c. progressive.
- d. proportional.
- 16. Structural unemployment
- a. occurs when workers voluntarily leave jobs for which
they are overqualified.
- b. can result when workers lose jobs that are becoming
obsolete.
- c. is considered less serious than frictional
unemployment.
- d. is a product of macroeconomic downturns.
- 17. When the economy is operating at full employment,
increased spending will result in
- a. profit-push inflation.
- b. wage-push inflation.
- c. cost-push inflation.
- d. demand-pull inflation.
- 18. Inflation would have benefited people
- a. who saved at fixed interest rates.
- b. who borrowed at fixed interest rates.
- c. who lent at fixed interest rates.
- d. who received fixed incomes.
- 19. Personal Income differs from Disposable Income by
- a. personal taxes.
- b. personal saving and personal taxes.
- c. net exports.
- d. personal saving.
- e. the rate of inflation.
- 20. Which of the following would be included in this
year's calculation of gross domestic product?
- a. repairs on your car done by yourself.
- b. a $2,000 fee to an attorney for legal fees.
- c. the purchase of a 1993 Corvette.
- d. a barter transaction between two students.
- 21. Suppose nominal GDP is $100 and the price index is
125. What is real GDP?
- a. $100
- b. $125
- c. $40
- d. $80
- 22. The consumption function illustrates that
- a. consumption increases as disposable income increases.
- b. consumption increases as disposable income decreases.
- c. saving increases as disposable income decreases.
- d. consumption increases as saving decreases.
- 23. The marginal propensity to consume is
- a. the level of household spending associated with a
given level of saving.
- b. the percentage of additional disposable income that
households spend.
- c. the same as autonomous consumption.
- d. always equivalent to the marginal propensity to save.
Use the Following Graph to Answer Question
24
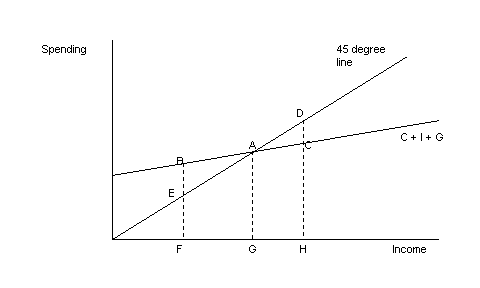
- 24. According to the graph above, the economy will
contract when aggregate expenditures are at
- a. point C.
- b. point D.
- c. point A.
- d. point B.
- e. point E.
- 25. If equilibrium income is $500 billion, MPC = 0.8, and
investment spending increases by $20 billion, the new
equilibrium income will be
- a. $600 billion.
- b. $700 billion.
- c. $520 billion.
- d. $550 billion.
- 26. Assume the economy is initially at full employment
with stable prices. Next, two things occur: (1)
businesses' expectations become more optimistic, and (2)
consumers decide to save less. To maintain stable prices
at full employment, appropriate discretionary fiscal
policy would consist of
- a. doing nothing as the two occurrences offset each
other.
- b. equal amounts of tax increase and government spending
increase.
- c. a tax increase and/or government spending decrease.
- d. a tax reduction and/or government spending increase.
- e. a decrease in the money supply and increase in
government spending.
- 27. Assume an MPC of 0.75 and a federal government
balanced budget. Congress enacts a lump sum tax reduction
of $40 billion. What will be the effect of this on GDP?
- a. $120 billion increase.
- b. $120 billion decrease.
- c. $40 billion increase.
- d. $40 billion decrease.
- e. $160 billion increase.
- 28. When the federal government is borrowing to finance a
deficit,
- a. there is no effect on GDP.
- b. exports will rise.
- c. the effect is to lower GDP.
- d. the effect is to increase GDP.
- 29. Which of the following is a reason why the U.S.
dollar is money?
- a. it has value as a commodity.
- b. it is backed by gold.
- c. it is generally accepted as a medium of exchange.
- d. it retains its value over time.
- 30. If a bank has deposits of $4,000,000, total reserves
equal to $600,000, and the reserve ratio is equal to
0.15, what is the value of excess reserves?
- a. $400,000.
- b. -$90,000.
- c. $600,000.
- d. $ 0.
- 31. The interest rate represents
- a. the index of creditworthiness for investors.
- b. the transactions demand for money.
- c. the opportunity cost of holding money.
- d. the market demand for bonds.
- 32. In the Classical quantity theory of money represented
by MV = PQ, a change in the money supply in the long run
will
- a. only change the price level.
- b. only change real GDP.
- c. cause real GDP (Q) to decrease.
- d. cause real GDP (Q) to increase.
- 33. Which of the following actions could the Fed take to
attempt to decrease the money supply?
- a. Decreasing the reserve requirement.
- b. Purchasing bonds.
- c. Selling bonds.
- d. Redefining the velocity of money.
- 34. The interest rate will decline when the Fed
- a. sells government securities on the open market.
- b. reduces the reserve requirement.
- c. increases the discount rate.
- d. increases the federal funds rate.
- 35. Which of the following monetary policies will
decrease spending?
- a. An increase in the reserve requirement.
- b. An increase in loans to the U.S. Treasury.
- c. Open market purchases of government securities.
- d. A decrease in the discount rate.
- 36. A point on the aggregate demand curve represents
- a. the amount of investment undertaken at a given
interest rate.
- b. the level of output demanded at a given price level.
- c. the amount of spending required to entice producers to
achieve a given output level.
- d. the cost of production associated with a given
production level.
- 37. If the economy is operating on the Keynesian range of
the Aggregate Supply curve, an increase in Aggregate
Demand will
- a. increase output only.
- b. increase output but decrease prices.
- c. increase prices only.
- d. increase both output and prices.
- 38. The Phillips curve suggests a short run trade-off
between
- a. monetary policy and fiscal policy.
- b. unemployment rates and inflation.
- c. unemployment rates and tax rates.
- d. inflation and the money supply.
- 39. When imports fall
- a. income rises.
- b. the government deficit rises.
- c. income falls.
- d. exports rise.
- 40. According to comparative advantage, trade between two
countries
- a. will benefit all the industries in each of the
countries.
- b. maximizes the amount of inputs that are used in the
production of all products.
- c. allows each of the trading countries to use its
resources most efficiently.
- d. guarantees that consumption levels will be equal in
the two countries.
 Back to the Final Exam Listings
Back to the Final Exam Listings


