Economics 155 Final Exam
Fall 1995
- 1. The main concern of economics is
- a. how to organize and run a business
- * b. how individuals and societies organize their scarce resources
- c. how to protect the consumer
- d. government spending and taxing
- 2. The most basic institution of a market system is:
- a. the existence of capital
- * b. private property
- c. the use of money
- d. production for the benefit of society, not individuals
- e. democracy
- 3. Which of the following is the primary incentive in determining WHAT to produce in a free
market price system? Produce those products that
- a. enjoy maximum freedom from government controls
- b. are needed by the masses of people
- c. are easiest to produce
- * d. will provide maximum profits for the producer
Use the graph below to answer question number 4
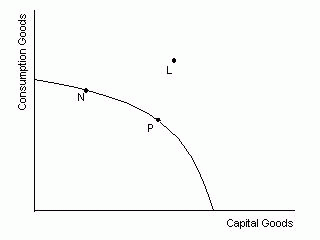
- 4. Other things being equal, society's current
choice of point P on the curve will:
- * a. allow it to achieve more rapid economic
growth than would the choice of point N
- b. entail a slower rate of economic growth than
would the choice of point N
- c. entail the same rate of growth as would the
choice of point N
- d. be unobtainable because it exceeds the
productive capacity of the economy
- 5. The production possibilities curve demonstrates
the basic principle that
- * a. given full employment of all of a nation's
resources, producing more of one good
necessarily entails producing less of another
- b. in a mixed capitalistic system with free
markets, the economy will automatically employ all of its resources
- c. exchange is a necessary corollary of specialization
- d. given full employment, to produce more of one good a nation will EVENTUALLY, but not
immediately, be forced to forgo production of other goods
- 6. The curvature in a production possibilities curve illustrates the law of
- a. comparative advantage
- * b. increasing costs
- c. constant costs
- d. decreasing costs
- e. of large numbers
- 7. If an increase in the price of product A results in an increase in the demand for product
B, one may conclude that products A and B are
- * a. substitute goods
- b. complementary goods
- c. unrelated goods
- d. inferior goods
- 8. Assume that Ford reduces the price of their subcompact and observes that their sales rise
while sales of Chevrolet's subcompact falls. Which of the following statements is
correct?
- a. Both Ford and Chevy experience an increase in the demand for their cars
- * b. Ford experiences an increase in quantity demanded while Chevy experiences a decrease
in demand
- c. Both Ford and Chevy experience changes in quantity demanded
- d. Ford experiences an increase in demand while Chevy experiences a reduction in
quantity demanded
- 9. With an increase in profits in a particular industry, we might expect
- a. firms to leave the industry
- b. firms to produce less
- * c. firms to enter the industry
- d. people to buy less
- e. profits don't have anything to do with what firms do
- 10. Which of the following will NOT change the demand for a good? A change in
- a. the number of consumers in the market
- b. the prices of related goods
- * c. the price of the good itself
- d. expectations about future prices
- 11. From an economic perspective, the complaint that there are not enough parking spaces in
downtown areas indicates that
- a. cities should build more parking places
- b. everyone should ride mass transit into the city
- c. the "market" for parking places is in equilibrium
- * d. the price of parking in downtown areas is below the market-clearing price
- 12. If supply and demand both decrease, we can say that equilibrium quantity:
- a. and equilibrium price must both decline
- * b. must decline, but equilibrium price may either rise, fall, or remain unchanged
- c. price must fall, but equilibrium quantity may either rise, fall, or remain unchanged
- d. and equilibrium price must both increase
- e. and equilibrium price must both decrease
- 13. Dairy price supports (floor) which raise milk prices received by farmers, are likely to:
- a. lower the price of milk
- b. result in shortages of milk
- c. help consumers
- * d. cause increased production of milk
- e. reduce inflation
- 14. Intermediate goods are excluded from GDP because
- a. intermediate goods go into inventories, and hence are not sold
- * b. their inclusion would lead to double counting
- c. they remain within the business sector
- d. none of the above
- 15. Let us consider that in 1950 the GDP was $500 billion while in 1960 GDP reached $700
billion, both in current (nominal) dollars. If the price index was lO0 in 1950 125 in
1960, what was the change in real GDP from 1950 to 1960? _____billion.
- a. zero
- b. $15
- c. $30
- d. $45
- * e. $60
- 16. Rent and interest are used to calculate
- a. indirect business taxes
- b. undistributed corporate profits
- * c. GDP by the income approach
- d. GDP by the expenditure approach
- 17. The sales tax is held to be a regressive tax because the:
- a. sales tax is an indirect, rather than a direct, tax
- b. tax tends to reduce the total volume of consumption expenditures
- c. percentage of income paid as taxes is constant as income rises
- d. administrative costs associated with the collection of the tax are relatively high
- * e. percentage of income paid as taxes falls as income rises
- 18. A common characteristic of pure public goods is that
- a. people pay for them in proportion to the benefits received
- b. the costs of producing them are less than if they were private goods
- * c. their benefits cannot be withheld from anyone, regardless of whether he pays for them
or not
- d. their benefits can be withheld from anyone who does pay for them
- e. they are produced only by the public sector, not by the private sector
- 19. The best estimate of about the current natural rate of unemployment is:
- a. 2 percent
- b. 3 percent
- * c. 6 percent
- d. 9 percent
- e. 0 percent
- 20. Inflation which is unexpected will most likely benefit:
- a. holders of cash
- b. creditors who lend funds to others
- c. those who have fixed incomes
- * d. people owing debts
- e. holders of U.S. Treasury bonds
- 21. Wendy Clark has stopped looking for a job, feeling that there are not any jobs available
for professional women television sportcasters like herself. She is
- a. frictionally unemployed
- b. cyclically unemployed
- *c. a discouraged worker
- d. a member of the labor force
Use the table below to answer question number 22
| Disposable Income | Consumption
|
| $ 400 | $ 405 |
| 450 | 450 |
| 500 | 495 |
| 550 | 540 |
| 600 | 585 |
- 22. The MPS is:
- a. 0.05
- b. 0.25
- c. 0.2
- d. 0.15
- * e. 0.1
- 23. The 45-degree line on a chart which relates consumption and income shows:
- a. the amounts households will plan to consume at each possible level of income
- b. the amounts households will plan to save at each possible level of income
- * c. all the points at which consumption and income are equal
- d. all points at which saving and income are equal
- 24. Assume the current equilibrium level of income is $200 billion as compared to the full
employment income level of $240 billion. If the MPC is 5/8, what change in autonomous
expenditures is needed to achieve full employment?
- * a. an increase of $15 billion
- b. an increase of $40 billion
- c. an increase of $10 billion
- d. an increase of $25 billion
- e. a decrease of $12 billion
- 25. The inequality of intended (planned) saving and intended (planned) investment:
- a. is of no consequence because actual saving and investment will always be equal
- b. is of no consequence because a compensating inequality of tax collections and
government spending will always occur
- * c. may be of considerable significance because of the subsequent changes in income,
employment, and the price level
- d. is attributable to a low MPC
- 26. If the MPC = 2/3 and if the government lowers taxes by $10 and increases government
expenditures by $5, then income would
- a. decrease by $5
- b. increase by $5
- * c. increase by $35
- d. decrease by $35
- e. increase by $45
- 27. Keynesian economics would attack demand pull inflation by:
- a. decreasing the tax rates and/or decreasing government spending
- b. decreasing the tax rates and/or increasing government spending
- c. increasing the tax rates and/or increasing government spending
- * d. increasing the tax rates and/or decreasing government spending
- 28. Suppose the economy is operating far below its full employment level. Now the government
increases its spending without an increase in taxes. Given time, this will most likely
result in:
- * a. output rising by a multiple of the increase in government spending and inflation may
increase a little
- b. a fall in output due to the initial position being one with idle resources
- c. no change in output but an increase in inflation
- d. a lowering of the rate of inflation
- 29. Assume Company X deposits $100,000 in cash in commercial bank A. If no excess reserves
exist at the time this deposit is made and the reserve ratio is 20 percent, Bank A can
safely increase the money supply by a maximum of:
- a. $100,000
- b. $500,000
- * c. $80,000
- d. $180,000
- e. $50,000
- 30. If the public finds ways of making the same amount of money perform a larger amount of
transactions than before
- a. the demand for money must have risen
- * b. velocity must have risen
- c. incomes and prices must have risen
- d. the supply of money must have risen
- 31. The "crowding-out effect" refers to possibility that
- * a. borrowing by the federal government crowds out private borrowing
- b. larger expenditures by the federal government simply crowd-out state and local
spending
- c. Congress has replaced the Federal Reserve System as the body mainly responsible for
monetary policy
- d. low income individuals are crowding middle income individuals out of the central city
into the suburbs
- 32. In the equation of exchange, if M = $200, P = $2, and Q = 400, then
- * a. V must be 4
- b. V must be one-half
- c. V must be 1
- d. V cannot be calculated with the available information
- e. the value of the goods and services produced in the economy must be $400
- 33. Which of the following best describes the Keynesian cause-effect chain of an easy
money policy?
- * a. an increase in the money supply will lower the interest rate, increase investment
spending, and increase GDP
- b. an increase in the money supply will raise the interest rate, decrease investment
spending, and decrease GDP
- c. a decrease in the money supply will raise the interest rate, decrease investment
spending, and decrease GDP
- d. a decrease in the money supply will lower the interest rate, increase investment
spending, and increase GDP
- 34. Open-market purchases of government securities by the Fed will have the tendency to
- a. increase interest rates, the money supply, and national income
- b. increase interest rates and the money supply, but decrease national income
- c. increase interest rates, but decrease the money supply and national income
- * d. decrease interest rates, but increase the money supply and national income
- e. decrease interest rates, the money supply, and national income
- 35. The Federal Funds market has reference to the market where:
- a. the federal government finances its debt
- * b. banks borrow reserves from other banks
- c. newly printed currency gets into circulation
- d. banks deposit the majority of their legal reserves
- e. checks are cleared
Use the graph below to answer question number 36
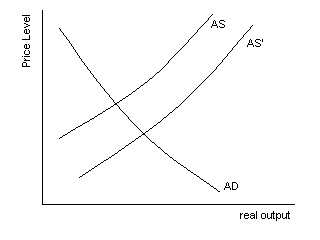
- 36. The shift in the Aggregate Supply
curve from AS to AS' shown here, could be
caused by all of the following except one.
Which is the EXCEPTION?
- a. increased preference for work
- b. development of new technology
- c. eductions in the availability of
unemployment compensation, welfare, etc.
- d. immigration of foreign nationals into
the U.S.
- * e. increased bargaining power of unions
- 37. Which of the following statements best
describes the relationship between total
output, total spending, and the general
price level?
- a. prices are stable until full employment
is reached; then any additional spending will be purely inflationary
- b. spending, output, and prices will always increase proportionately
- * c. for a time increases in spending will cause large increases in output and little
or no increase in prices; but as full employment is approached prices begin to
rise more rapidly
- d. spending and output are directly related; but spending and prices are inversely
related
- 38. Which of the following is not essential for the classical model to be valid?
- a. wage-price flexibility
- b. interest rate flexibility
- c. long-run full employment
- * d. fixed money supply
- 39. To say that a country has a comparative advantage in the production of wine is to
say that
- a. it can produce wine with fewer resources than any other country can
- b. its opportunity cost of producing wine is greater than any other country's
- * c. its opportunity cost of producing wine is lower than any other country's
- d. the relative price of wine is higher in that country than in any other
- 40. When U.S. exports exceed U.S. imports this has the effect of acting:
- a. to raise the U.S. unemployment rate
- b. as a net leakage
- * c. in a manner similar to other injections as investment and government spending
- d. to weaken the dollar exchange rate - i.e. - the dollar depreciates
- e. to cause American producers to lose profits
 Back to the Final Exam Listings
Back to the Final Exam Listings



