Economics 155 Final Exam
Spring 1998
- 1. Which one of the following quotations provides the
best example of a positive as opposed to a
normative economic statement?
- a. "General Motors is too large a company, and it
would be better for everyone if it were broken up into
competing firms."
- b. " The government needs to do all that it can to
provide economic assistance for the weak and the
poor."
- c. "The poor deserve better economic opportunities
than they have had thus far."
- d. "A general 5 percent reduction in the price of
automobiles would increase the sale of automobiles by at
least 2 percent."
- e. "What this country needs is a 5 cent beer."
- 2. When Adam Smith spoke of the principle of the
"invisible hand", he meant:
- a. the pursuit of one's own self-interest will lead to
the best good for all
- b. cooperation among producers is necessary to minimize
losses
- c. governmental intervention in the marketplace may be
necessary to have steady growth in national output
- d. that the government regulates all firms in such a
manner that the "social responsibility" of
business is assured
- e. that although the government dominates our economy,
most of us are not aware of this fact
- 3. The fundamental economic questions ("what",
"how", and "for whom") must be solved
in:
- a. market economies
- b. mixed economies
- c. planned (command) economies
- d. all of the above
- e. none of the above
- 4. On a production possibilities curve, the optimum or
best combination of output is
- a. at a point near the top of the curve
- b. at a point near the middle of the curve
- c. at the precise midpoint of the curve
- d. at a point near the bottom of the curve
- e. impossible to say as this is a value judgment to be
made by society
- 5. A 'straight-line' production possibility curve differs
from a concave (or 'bowed-out') production possibility
curve in which of the following ways?
- a. the 'bowed-out' production possibility curve has a
constant opportunity cost, whereas the 'straight-line'
production possibility curve does not
- b. a 'straight-line' production possibility curve has a
constant opportunity cost, whereas the 'bowed-out'
production possibility curve does not
- c. the 'straight-line' production possibility curve does
not show scarcity, whereas the 'bowed-out' production
possibility curve does
- d. a 'straight-line' production possibility curve must be
'upward-sloping to the right' to reflect the law of
increasing costs
- 6. Which of the following would not be an example
of capital:
- a. oil refinery in New Jersey
- b. shipyard in San Francisco
- c. Great Southern Savings and Loan building
- d. undeveloped oil field in Oklahoma
- e. steel mill in Pittsburgh
- 7. Assume that the Fairweather Shoe Company faces a
downward sloping demand curve. In March it sold 1000
pairs of shoes at $30 a pair, but during the following
month it was able to sell only 500 pairs at the same
price. It may be concluded that during this time period
the company had
- a. an increase in the quantity demanded
- b. an increase in demand
- c. a decrease in demand
- d. a decrease in the quantity demanded
- e. none of the above
- 8. If the demand curve for product B shifts to the right
as the price of product A declines, it can be concluded
that:
- a. A and B are substitute goods
- b. A and B are complementary goods
- c. A is an inferior good and B is a superior good
- d. A is a superior good and B is an inferior good
- e. both A and B are inferior goods
- 9. Which of the following will NOT shift the demand curve
for grapefruit?
- a. An announcement that eating grapefruit before every
meal will induce weight loss.
- b. An announcement that the workers who harvest
grapefruit are demanding higher wages.
- c. An announcement that eating lots of grapefruit causes
complexion problems.
- d. An announcement that grapefruit will definitely cost
more next week.
- e. A newspaper story reporting that the price of oranges
has skyrocketed
- 10. When income increases and the demand for a particular
good also increases, we call the good in question
- a. an inferior good
- b. a normal good
- c. a substitute good
- d. a complementary good
- 11. The establishment of an effective price floor
(support) can be expected to bring about quantity
supplied
- a. equal to the quantity demanded
- b. greater than the quantity demanded
- c. less than the quantity demanded
- d. none of these
- 12. An increase in the wage paid to grape pickers will
cause the
- a. demand curve for grapes to shift to the right --
resulting in higher price for grapes and a reduction in
amount consumed
- b. demand curve for grapes to shift to the left resulting
in higher price for grapes and a reduction in amount
consumed
- c. supply curve for grapes to shift to the left --
resulting in lower price for grapes and reduction in
amount consumed
- d. supply curve for grapes to shift to right -- resulting
in lower price for grapes and increase in amount consumed
- e. supply curve for grapes to shift to left -- resulting
in higher price for grapes and decrease in amount
consumed
- 13. If the industry demand curve for sports cars shifts
sharply to the left as the industry supply curve for
sports cars moves to the right, we would expect:
- a. the same price for sports cars to prevail
- b. the same quantity of sports cars sold to prevail
- c. price and quantity of sports cars to fall
- d. price of sports cars to fall while the quantity sold
may or may not change
- e. quantity of sports cars to fall while the price may or
may not change
- 14. Historically, real GDP has risen less rapidly than
money GDP because:
- a. exports to foreign nations have risen more rapidly
than imports
- b. the general price level has fallen
- c. technological progress has resulted in more efficient
production
- d. the general price level has risen
- e. price indices have not reflected improvements in
product quality
- 15. If the price index is 225.1, this means that:
- a. prices are 125.1 percent higher than in the base year
- b. money GDP is the same as real GDP
- c. the inflation rate is 225.1 percent higher than in the
base year
- d. any basket of goods costs $125.10 more in terms of a
base year
- 16. Real income differs from money income in that real
income:
- a. refers to earned income, while money income refers to
unearned income
- b. refers to income minus the amount put into savings,
while money income includes savings
- c. reflects constant dollar purchasing power, while money
income reflects current dollar purchasing power
- d. represents the income value used in determining income
taxes, while money income is the gross income actually
received before taxes
- 17. A particular tax takes $400 from the Brown family
which has an income of $16,000. The Millers have an
income of $40,000 and the same tax takes $800 from them.
Miller attempts to convince Brown that this tax is
progressive. Is Miller correct?
- a. yes, since the tax takes more from his family it is
progressive
- b. no, this is a proportional tax
- c. no, the tax is actually regressive
- d. no, the tax is degressive
- e. uncertain, we need to know the tax in relation to
wealth to be able to say if it is progressive,
regressive, or proportional
- 18. Which of the following statements is correct?
- a. Public goods are divisible among individual consumers,
bought voluntarily out of private incomes, and yield
widespread social benefits
- b. Private goods are indivisible among individual
consumers, bought voluntarily out of private incomes, and
yield no significant social benefits
- c. Public goods are indivisible among consumers, yield
widespread social benefits, and may be purchased by
government with tax revenues
- d. Private goods are divisible among consumers, yield
direct benefits to the purchaser and are financed by
government
- 19. When full employment exists:
- a. everybody is working
- b. there is a very high level of employment, with the
unemployed being largely frictionally unemployed
- c. frictional unemployment is virtually zero
- d. the only people who are unemployed are those who
refuse to accept jobs at the going wage
- 20. During a period of unanticipated high inflation
- a. borrowers are better off because they can pay off
their loans with currency that is worth less
- b. borrowers are better off because they have to pay off
their loans with currency that is worth more
- c. lenders are worse off because they cannot find anyone
who wants a loan
- d. lenders are worse off because they are repaid with
currency that is worth more
- e. lenders are better off because they are repaid with
currency that is worth less
- 21. The main difference between the consumer price index
and the implicit GDP price deflator is that the former:
- a. collects information on consumer goods only and the
latter on producer goods only
- b. measures price increases and the latter measures price
decreases
- c. deals with nondurable goods and the latter deals with
durable goods
- d. deals with a typical basket of consumer goods and the
latter deals with the whole range of products produced in
an economy
- 22. If disposable income rises from $600 billion in year
1 to $650 billion in year 2 and household consumption
subsequently increases from $540 billion in year 1 to
$570 billion in year 2, the average propensity to consume
in year 1 was
- a. 0.60
- b. 0.70
- c. 0.80
- d. 0.90
- e. none of the above
Use the following table to answer
question 23
GDP
|
C
|
I
|
2000
|
1430
|
540
|
1900
|
1360
|
540
|
1800
|
1290
|
540
|
1700
|
1220
|
540
|
1600
|
1150
|
540
|
- 23. From the table above (quantities in $billions), we
know that:
- a. when GDP is less than 1,600, it will fall
- b. when GDP is greater than 2,000, it will rise
- c. the multiplier is 2.5
- d. when GDP = 1900, the economy is in equilibrium
- e. all the above are confirmed
- 24. The unplanned accumulation of inventory is a sign
that:
- a. aggregate expenditure exceeds current national income
- b. planned investment exceeds planned saving
- c. planned investment equals planned saving
- d. current national income exceeds aggregate expenditure
- 25. Suppose the economy is in equilibrium when total
spending is $3600 billion and the MPC is 0.60. Full
employment can be achieved if total spending is $4200
billion. To achieve this, government spending should be
increased by billion.
- a. $500
- b. $225
- c. $100
- d. $240
- 26. The tools of government fiscal policy include all of
the following except:
- a. government spending on goods and services
- b. changes in the money supply
- c. changes in tax rates
- d. the imposition of new taxes
- e. changes in welfare payments
- 27. If the MPC equals .75 and Government expenditures increase
by $20 and Taxes decrease by $30, income will:
- a. increase by $200
- b. decrease by $200
- c. increase by $170
- d. decrease by $170
- e. none of these are correct
- 28. An effective countercyclical fiscal policy would
include:
- a. raising government expenditures and raising taxes in
times of expansion
- b. raising government expenditures and cutting taxes in
times of recession
- c. raising government expenditures and cutting taxes in
times of expansion
- d. reducing government expenditures and raising taxes in
times of recession
- e. none of the above would be effective
- 29. In the most basic sense, paper money and demand
deposits are valuable because:
- a. the government or central bank "prints" them
- b. there is gold to back them
- c. people think there is gold to back them
- d. people can buy goods and/or services with them
- e. people are ordered to use them
- 30. Suppose the required reserve ratio is 10 percent.
Then, an increase in the banking system's excess reserves
by $l,000 may result in a total expansion of the money
supply for the banking system as a whole by as much as:
- a. $1,000
- b. $10,000
- c. $100,000
- d. $9,000
- e. $90,000
- 31. To solve the demand-pull inflation problem, the
"Monetarists" recommend the Federal Reserve
- a. decrease the rate of growth of the money supply
- b. increase interest rates and also increase the money
supply
- c. increase taxation and decrease government expenditure
- d. increase interest rates and buy government securities
- 32. In the Keynesian view, the link between the money
supply and changes in real macroeconomic variables is
best described by
- a. a change in interest rates that induces a change in
investment spending, a change in aggregate demand, and
thus an immediate and unavoidable change in real GDP.
- b. a change in interest rates that induces a change in
investment spending, a change in aggregate demand, and
thus a potential change in real GDP.
- c. a change in investment spending caused directly the
Fed's adjusting its own investment portfolio and which
translates into a change in aggregate demand and finally
a change in GDP
- d. a change in banker's interest rates by direct
intervention that may or may not alter real GDP by
altering investment spending
- e. none of the above
- 33. In a particular year we were experiencing 8 percent
unemployment, real GDP was decreasing by 0.5 percent and
the rate of inflation was less than 1 percent. In this
situation, appropriate fiscal and monetary policy would
consist of:
- a. a tax cut and sale of government securities on the
open market
- b. a tax cut and purchase of government securities on the
open market
- c. a tax increase and decrease of the discount rate
- d. balance the federal budget and sale of government
securities on the open market
- e. a decrease in government spending and decrease reserve
requirements
- 34. If the Federal Reserve authorities were attempting to
reduce inflationary pressures, the proper policies would
be to government securities, reserve requirements, and
the discount rate.
- a. sell; raise; lower
- b. sell; lower; lower
- c. buy; raise; raise
- d. sell; raise; raise
- 35. Assume that today no bank has excess reserves and the
reserve requirement is 20%. Tomorrow the Federal Reserve
cuts the reserve requirement to half of its initial
level. Which of the following is true after the
reduction?
- a. banks will be enabled to make new loans
- b. excess reserves will exist in banks
- c. the Fed exercised expansionary policy
- d. all of the above
- e. none of the above
Use the following graph to answer
question 36
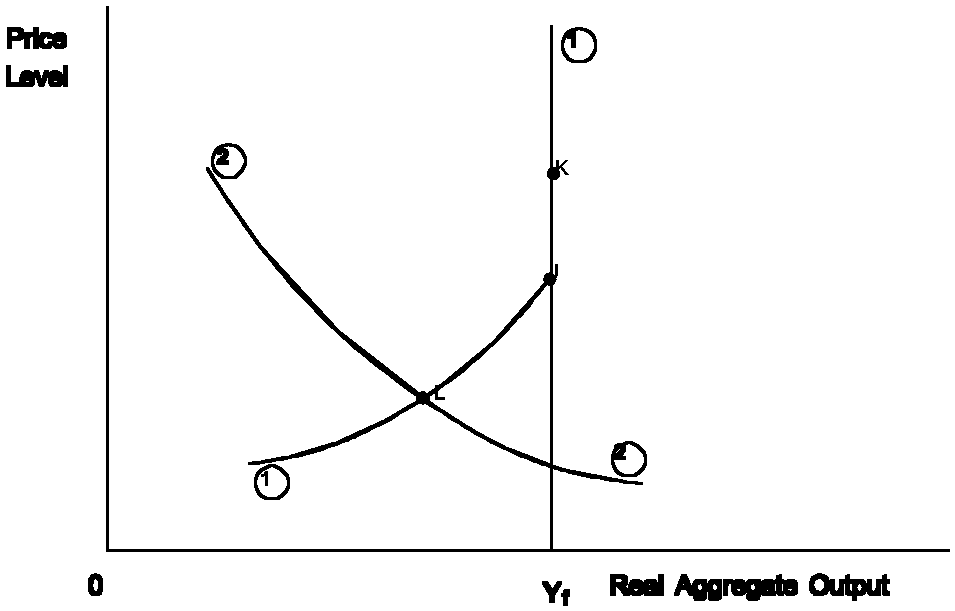
- 36. Suppose government ends its regulations for certain
areas, fostering improvements in worker productivity.
Initially, this shows up in the diagram as:
- a. a leftward shift in curve 1
- b. a leftward shift in curve 2
- c. a rightward shift in curve 1
- d. a rightward shift in curve 2
- 37. According to the Keynesian view, along which portion
of the aggregate supply curve will a given increase in
aggregate demand have the least inflationary and greatest
employment effects?
- a. the horizontal portion of the aggregate supply curve
- b. the upward sloping portion of the aggregate supply
curve
- c. the vertical portion of the aggregate supply curve
- d. none of the above
- 38. Stagflation is the combination of
- a. high inflation and high employment
- b. high inflation and high taxes
- c. high inflation and high unemployment
- d. high inflation and high interest rates
- e. none of the above describe the term stagflation
- 39. An increase in US exports and/or a decrease in US
imports will cause
- a. an increase in aggregate expenditures
- b. a decrease in aggregate expenditures
- c. no impact on aggregate expenditures
- d. no impact on the economy
- 40. Suppose that with the same resources, the U.S. can
produce 50 barrels of oil or 50 tons of wheat; Saudi
Arabia can produce 100 barrels of oil or 80 tons of
wheat.
- a. Saudi Arabia has comparative advantage in both goods
- b. The U.S. has comparative advantage in both goods
- c. The U.S. has comparative advantage in wheat
- d. Saudi Arabia has comparative advantage in wheat
 Back to the Final Exam Listings
Back to the Final Exam Listings

