Economics 155 Final Exam
Spring 1995
- 1. During a concert at Hammons Center, a large number of patrons decided to leave 20
minutes early to avoid traffic congestion getting away from campus to late evening
"study" spots. Due to the large number involved in the exodus, there was
considerable congestion in the parking area before the concert was over. This
occurrence depicts which of the following?
- a. Murphy's Law
- b. post hoc fallacy
- c. law of diminishing returns
- * d. fallacy of composition
- e. law of increasing costs
-
2. An editor of a local newspaper called for the government to abolish the minimum wage
because it takes advantage of consumers. This is an example of:
- a. a positive economic statement
- b. a pure economic statement
- c. an exogenous use of economics
- * d. a normative economic statement
- e. an abstract economic statement an exogenous use of economics
-
3. Which of the following is the primary incentive in determining WHAT to produce in
a free market price system? Produce those products that
- a. enjoy maximum freedom from government controls
- b. are needed by the masses of people
- c. are easiest to produce
- * d. will provide maximum profits for the producer
Use the table below to answer question number 4
| Alternative | Pizza |
Beer |
| A | 0 |
100 |
| B | 10 |
95 |
| C | 20 |
80 |
| D | 30 |
60 |
| E | 40 |
35 |
| F | 50 |
0 |
- 4. The opportunity
cost of each of the 11th through l9th units of
pizza is approximately:
- a. 10 units of beer
- * b. 1.5 units of beer
- c. 2 units of beer
- d. 80 units of beer
- e. none of the above
-
5. Assuming an economy to be operating at a point
inside the production possibilities line, one
may conclude that:
- a. the economy is at full employment
- b. maximum output is now achieved
- * c. unemployment or underemployment exists
- d. the economy is of a command type
-
6. The law of increasing opportunity costs states that:
- a. if the prices of all the resources devoted to the production of goods increase,
the cost of producing any particular good will increase at the same rate
- b. if the sum of the costs of producing a particular good rises by a specified
percent, the price of that good must rise by a greater relative amount
- c. the sum of the costs of producing a particular good cannot rise above the
current market price of that good
- * d. if society wants to produce more of a particular good, it must sacrifice larger
and larger amounts of other goods to do so
-
7. If the price of product L increases, the demand curve for a close substitute product
M will:
- a. remain unchanged
- * b. shift to the right
- c. shift to the left
- d. none of the above
-
8. Other things being unchanged, a decrease in the supply of X might be caused by:
- a. an improvement in the technology for producing X
- b. an increase in the number of firms producing X
- c. a decline in the price of the basic raw material used in producing X
- d. a government subsidy per unit of output, paid to firms producing X
- * e. an increase in the wages paid to laborers employed in the production of X
-
9. The demand for parking spaces on this campus is very high. If we were to raise the
price of a parking sticker, we would decrease the demand. This statement:
- a. confuses a change in quantity demanded with a movement along the demand curve
- b. is correct as stated
- c. confuses the determinants of demand with the determinants of supply
- * d. confuses a change in quantity demanded with a change in demand
-
10. With an increase in profits in a particular industry, we might expect
- a. firms to leave the industry
- b. firms to produce less
- * c. firms to enter the industry
- d. people to buy less
- e. profits don't have anything to do with what firms do
Use the graph below to answer question number 11
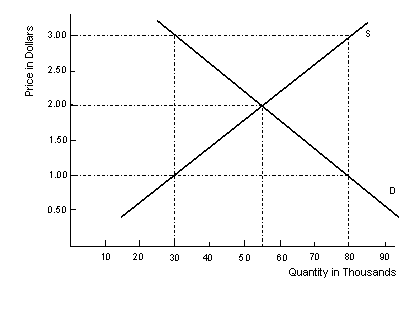
-
11. Using the graph above, a price of $1.00 per
unit will result in:
- * a. a shortage of 50 units
- b. a surplus of 80 units
- c. a shortage of 80 units
- d. a surplus of 50 units
- e. impossible to say without more information
-
12. Given the standard supply-and-demand diagram, which of
the following statements is correct? (Hint: draw
diagrams)
- a. If supply shifts left and demand remains
constant, equilibrium price will fall
- b. If supply shifts right and demand remains
constant, equilibrium price will rise
- c. If demand shifts left and supply shifts right, equilibrium price will rise
- d. If supply shifts right and demand shifts right even more, equilibrium price
will fall.
- * e. none of the above
-
13. A price ceiling is
- * a. a maximum legal price
- b. the only legal price
- c. a minimum legal price
- d. the legal price of housing
-
14. Real GDP (or GDP in "constant dollars") means
- * a. GDP has been adjusted for price level changes
- b. GDP is not changing
- c. GDP has been corrected for quality changes
- d. prices have not changed
- e. GDP has been corrected for changes in tastes
-
15. Which of the following items is excluded from the calculation of GDP:
- a. the purchase of 100 shares of General Motors stock
- b. the sale of 100 shares of General Motors stock
- c. the value of a housewife's services
- d. the sale of unused military surplus
- * e. all of these
-
16. GDP attempts to measure economic activity by avoiding double-counting. Which of the
following would be an example of double-counting?
- * a. Counting both the value of a carpenter's labor and the value of the new house
that he produces.
- b. Counting the real estate agent's commission on the sale of a house.
- c. Counting the cost of government paid street improvements.
- d. All of the above would be double-counting.
-
17. An income tax may be called progressive when:
- a. the tax rate on low-income groups exceeds the tax rate of high-income groups
- b. high-income groups pay more taxes absolutely than do low-income groups
- * c. the tax rate increases as income goes up
- d. the tax rate is constant, but the absolute amount of taxes paid increases, as
income goes up
-
18. Suppose a person earning $20,000 a year is paying $2,000 in income taxes. If the
marginal tax rate is 15%, what will his year's income taxes be if he takes a
temporary part-time job earning $2,000 additional income?
- a. $3,300
- b. $300
- c. $3,000
- * d. $2,300
- e. not possible to calculate given the information
-
19. In the official statistics, a worker who is so discouraged that he has stopped
looking for employment is counted as:
- a. unemployed
- b. in the labor force, but not employed
- c. underemployed
- * d. not in the labor force
- e. none of the above
-
20. The Consumer Price Index rose from 340 in 1987 to 354 in 1988. The inflation rate
from l987 to 1988 was:
- a. 14 percent
- b. 7 percent
- * c. 4.1 percent
- d. 3.54 percent
- e. less than 2 percent
-
21. In order to produce more fuel efficient cars, U.S. auto makers have used less steel
and more light weight materials. The unemployment it causes in the steel industry
is an example of:
- a. cyclical unemployment
- b. seasonal unemployment
- * c. structural unemployment
- d. frictional unemployment
- e. unnatural unemployment
Use the table below to answer question number 22
Disposable
Income | Consumption
|
| $400 | $405 |
| $450 | $450 |
| $500 | $495 |
| $550 | $540 |
| $600 | $585 |
-
22. The MPC is:
- a. 1.2
- * b. 0.9
- c. 0.8
- d. 0.75
- e. 0.66
-
23. If investment spending increases by $8 billion
and the MPS equals .25, the level of GDP
(income) will increase by ______ billion.
- a. $14
- * b. $32
- c. $28
- d. $12
- e. $2
-
24. Which of the following relationships is NOT correct?
- a. MPC + MPS = 1
- b. 1 - APC = APS
- * c. MPS = MPC + 1
- d. APS + APC = 1
- e. 1 - MPC = MPS
-
25. Autonomous consumption:
- a. is consumption that will occur at income levels beyond the break-even level of
income
- * b. is consumption which will occur independent of the level of income
- c. is represented as the intersection of the consumption function with the income
axis
- d. varies with the level of income
-
26. If the economy is at full employment and the government increases spending on
defense programs, which of the following actions will prevent inflationary
pressures?
- * a. increase taxes by an amount greater than the increased defense spending
- b. decrease the welfare program by an amount equal to the increase in defense
spending
- c. issue bonds to finance the defense spending
- d. decrease social security payments by an amount equal to the increase in defense
spending
- e. the government can avoid an inflation simply by doing nothing further
-
27. Which of the following fiscal actions is likely to be most effective in curbing
inflation?
- a. incurring a budget surplus which is used to retire debt held by the public
- * b. incurring a budget surplus and allowing that surplus to accumulate as idle
treasury balances
- c. incurring a budget surplus which is used to retire debt held by commercial
banks
- d. incurring a budget deficit by borrowing from the public
- e. shifting federal spending away from nonproductive spending such as social
security and into spending such as national defense
-
28. If the government ceases to balance the budget by engaging in deficit spending
during a period of full employment:
- a. unemployment will tend to result
- * b. inflation will tend to result
- c. debt can be reduced
- d. interest rates will automatically decline
- e. a deflationary gap will result
-
29. Assume that Smith deposits $600 in currency in his checking account at the XYZ Bank.
Later the same day Jones receives a loan for $l,200 at the same bank. In what
direction and by what amount has the supply of money changed following these two
transactions?
- * a. increased by $1,200
- b. increased by $600
- c. increased by $1,800
- d. decreased by $600
- e. decreased by $l,200
-
30. If the public finds ways of making the same amount of money perform a larger amount
of transactions than before
- a. the demand for money must have risen
- * b. velocity must have risen
- c. incomes and prices must have risen
- d. the supply of money must have risen
-
31. Suppose that the banking system holds $1 million in demand deposits and $300,000 in
legal reserves.If the required reserve ratio is 20 percent, he maximum amount by
which the banking system can expand the money supply is:
- a. $100,000
- * b. $500,000
- c. $1,000,000
- d. $1,500,000
- e. $2,000,000
-
32. In order to serve as money, a thing must
- a. be officially issued by the government
- b. consist of, or be legally exchangeable for gold
- c. have a stable purchasing power in exchange for goods and services
- * d. be generally accepted in a given society in exchange for goods and services
- e. have the faith and confidence of the public in the ability of the government
to pay its debt
-
33. In controlling the money supply, the Federal Reserve System most uses:
- * a. open market operations
- b. changes in the discount rate
- c. changes in reserve requirements
- d. moral suasion
- e. changes in Regulation Q
-
34. Open-market purchases of government securities by the Federal Reserve System will
have the tendency to
- a. increase interest rates, the money supply, and national income
- b. increase interest rates and the money supply, but decrease national income
- c. increase interest rates, but decrease the money supply and national income
- * d. decrease interest rates, but increase the money supply and national income
- e. decrease interest rates, the money supply, and national income
-
35. Which of the following actions by the Fed is likely to be contractionary?
- a. decreasing reserve requirements
- b. decreasing the discount rate
- * c. selling bonds in the open market
- d. decreasing margin requirements
- e. all of these
Use the graphs below to answer question number 36
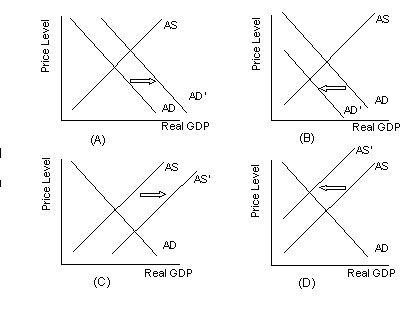
-
36. Which diagram above depicts a new
equilibrium price level and real GDP if the
price of crude oil drops from $17.00 per
barrel to $4.00 per barrel?
- a. diagram a
- b. diagram b
- * c. diagram c
- d. diagram d
-
37. If an economy is already experiencing
inflation, efforts to reduce unemployment by
stimulating aggregate demand are most likely
to cause:
- a. the unemployment rate to rise in the
short run
- * b. the inflation rate to accelerate
- c. a decline in the price level, coupled
with a sharp increase in unemployment
- d. real income to expand, but money income is likely to remain unchanged
-
38. The classical view of high unemployment levels is that:
- a. fiscal policy will be of no corrective use in the economy
- b. only fiscal policy can revive economic growth
- * c. flexible wages and prices will eventually reduce unemployment
- d. higher prices will generate higher profits, allowing additional investment to
take place
-
39. The value of net exports is:
- * a. an injection into the economy if exports exceed imports
- b. an injection into the economy if imports exceed exports
- c. always positive
- d. always larger than government expenditures
-
40. According to the principle of comparative advantage, a particular task will be
performed most efficiently the party with the
- a. lowest absolute advantage
- b. largest production possibility curve
- c. largest absolute advantage
- * d. lowest opportunity cost
- e. highest tariff
 Back to the Final Exam Listings
Back to the Final Exam Listings



