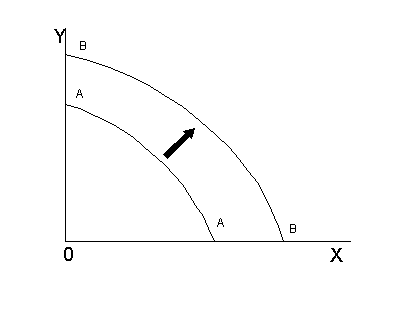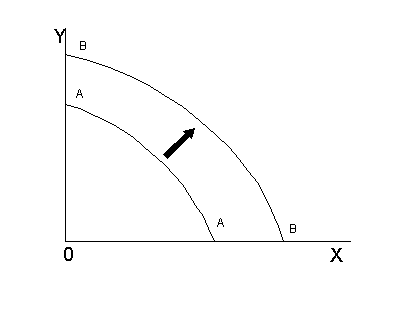Economics 165 Final Exam
Fall
1995
- 1. Opportunity costs are the values of the:
- a. minimal budgets of families on welfare
- b. hidden charges passed on to consumers
- c. monetary costs of goods and services
- d. best alternatives sacrificed when choices are made
- e. exorbitant profits made by greedy
entrepreneurs
-
2. A mixed economy is one where
- a. the system changes from purely a free market
economy to purely a control
economy
- b. the market system handles resource allocation
- c. there are elements of democracy and dictatorship
- d. there are elements of a free market economy and a
control (planned) economy
Use the graph below to answer question number
3
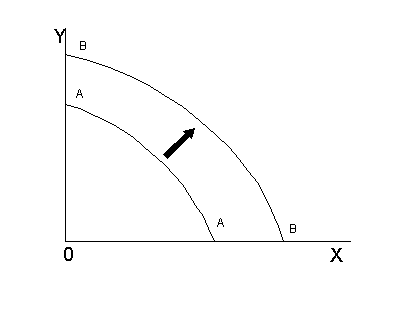
-
3. According to the graph above, a shift in
the production-possibilities frontier from A-A to
B-B could result from:
- a. improved technology in the production of
both goods
- b. changes in the combination of goods
produced
- c. unemployment
- d. inflation
- e. changes in consumers' tastes
-
4. A certain country produces only two goods, A and
B. A change in government policy results in the
society being able to enjoy more of good A
without having to sacrifice any of good B. This
situation:
- a. suggests that before the policy change the economy
was either operating
inefficiently or had unemployed resources
- b. demonstrates that all economic problems are
inter-related
- c. demonstrates the law of scarcity
- d. indicates that government was able to temporarily
push society beyond its
potential
-
5. Which one of the following will cause the demand curve for
gasoline to shift to the
right?
- a. a fall in the price of cars
- b. an increase in the supply of gasoline
- c. a fall in the price of gasoline
- d. a rise in the price of cars
-
6. If the price of product 'X' decreases, the demand for a
close substitute product
'Y':
- a. is inelastic
- b. will shift to the left
- c. will not be affected
- d. is elastic
-
7. To say that oatmeal is an inferior good, as economists use
the term
- a. means that as the price of oatmeal falls, the
quantity demanded of oatmeal
falls
- b. means that there is no real income effect when
the price of oatmeal changes
- c. provides an example of a normative statement
- d. means that as the average level of income falls,
the demand for oatmeal rises
- e. means that the supply of oatmeal is perfectly
inelastic
-
8. Assuming that over the last three years the equilibrium
quantity of wheat has risen
while over the same period the equilibrium price has not
changed, which of the
following is the most likely explanation of these facts?
- a. An increase in the number of consumers and a
reduction in input prices
- b. A reduction in the price of a substitute for
wheat and a reduction in input
prices
- c. A reduction in consumers' income wheat is a
normal good and an increase in
input prices
- d. An increase in consumers' income wheat is a
normal good and an increase in
input prices
-
9. Price ceilings and price floors are usually intended to
benefit:
- a. government by increasing government revenue
- b. buyers (ceilings) and sellers (floors)
- c. buyers
- d. sellers
-
10. If the percentage change in quantity demanded for a product
is smaller than the
percentage change in price, then demand for the good is
- a. infinitely elastic
- b. of unitary elasticity
- c. perfectly inelastic
- d. inelastic
- e. elastic
-
11. Two goods are complements in consumption if:
- a. both are inferior goods
- b. the cross elasticity of demand between them is
negative
- c. both have negative price elasticities
- d. one has a positive elasticity and the other has
a negative price elasticity
-
12. Utility analysis suggests that
- a. a consumer will purchase only one good at a time
- b. there is an inverse relationship between price and
quantity demanded
- c. the law of demand is nonsense
- d. a consumer will always purchase goods in pairs
-
13. Consumers' surplus means
- a. total expenditure divided by the price per unit
- b. the difference between the maximum price a
consumer would have been willing
to pay for a good and the actual price paid
- c. value in use
- d. value in exchange
-
14. The demand for a foreign currency results primarily from
the:
- a. supply of domestically produced goods and
services
- b. demand for goods and services produced
domestically
- c. supply of that foreign currency at a given
exchange rate
- d. demand for foreign goods and services
-
15. A tax imposed only on an imported good is a
- a. subsidy
- b. embargo
- c. quota
- d. tariff
-
16. The cost that does NOT vary with the quantity of output that
a firm produces is
- a. average variable cost
- b. average fixed cost
- c. total variable cost
- d. total cost
- e. total fixed cost
-
17. The meaning of the term "marginal cost" is most closely
described by which of the
following statements?
- a. unavoidable expenditures that must be paid
regardless of the firm's output
- b. the increase in total costs which occurs if output
increases by one unit
- c. total variable cost divided by quantity
- d. the total costs associated with producing some
specific level of output
-
18. A driver wishes to buy gasoline and have his car washed. He
finds that the market
price of gasoline is $1.08 and that the wash costs $1.00
when he buys 19 gallons
but that if he buys 20 gallons, the car wash is free. The
marginal cost of the
twentieth gallon is:
- a. $1.00
- b. zero
- c. 8 cents
- d. $1.08
-
19. In the short run, if average variable costs equal $6 and
average total costs equal
$10 and output equals 100, then total fixed costs equal:
- a. $16
- b. $1,600
- c. $4
- d. $400
- e. $0.025
-
20. The factors which cause economies and diseconomies of scale
help explain
- a. why the firm's long-run average total cost curve
is U-shaped
- b. the profit-maximizing level of production
- c. the distinction between fixed and variable costs
- d. why the firm's short-run marginal cost curve cuts
the short-run average
variable cost curve at its minimum point
-
21. The additional revenue a firm receives from selling an extra
unit of output is
- a. average revenue
- b. marginal profit
- c. total revenue
- d. marginal revenue
- e. price
-
22. If a perfectly competitive firm sells 250 units of output at
a market price of 55
dollars per unit, its marginal revenue is:
- a. $55
- b. $110
- c. more than $55 but less than $13,750
- d. less than $55
-
23. A profit-maximizing firm will produce that level of output
where
- a. marginal revenue equals marginal cost
- b. marginal cost equals marginal product
- c. price equals average cost
- d. price equals variable cost
- e. marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost by the
maximum amount
-
24. In the short run if a profit-maximizing firm is incurring
losses, it will
- a. produce if it can cover its fixed costs
- b. produce if price exceeds average variable cost
- c. shut down
- d. go out of business
-
25. When firms leave a perfectly competitive market, other
things equal,
- a. market demand will increase and market price will
rise
- b. market demand will decrease and market price will
fall
- c. market supply will decrease and market price will
rise
- d. market supply will decrease and market price will
fall
-
26. Which of the following is characteristic of perfectly
competitive firms in long-run
equilibrium?
- a. firms experience diseconomies of scale
- b. firms produce at minimum average total cost
- c. price exceeds marginal cost
- d. firms earn positive economic profit
-
27. Assume that at the current output level, a monopolist is
breaking even (profit
equals zero), has a marginal revenue of $7, and a marginal
cost of $4. Which of the
following statements is correct?
- a. The firm could increase its profit by increasing
its output
- b. The firm could increase its profit by decreasing
its output
- c. The firm is producing the profit-maximizing
output
- d. The firm could increase its profit by increasing
its price
-
28. If a monopolist lowers price and total revenues rise, then
- a. average revenue must be less than marginal
revenue
- b. there must be no close substitutes for the
monopolist's product
- c. the monopolist must be in the inelastic region of
its demand curve
- d. the marginal revenue must be positive
-
29. Two of the characteristics of monopolistic competition are
- a. many firms, identical products
- b. many firms, different products
- c. a single firm, several products
- d. a single firm, one product
-
30. In monopolistic competition, the demand curve facing a firm
will become more elastic
the:
- a. greater the obstacles to entry
- b. greater the elasticity of its supply curve
- c. greater the number of sellers
- d. fewer the number of sellers
-
31. The number of firms in an oligopoly must be
- a. large enough that firms cannot closely monitor
each other
- b. small enough that firms are interdependent in
decision making
- c. less than a dozen
- d. large enough that firms cannot collude
- e. large enough that firms will see no reason to
engage in nonprice competition
-
32. If a cartel determines the profit-maximizing quantity for
the whole group, it will
choose the quantity at which
- a. price is highest
- b. cost is lowest
- c. marginal cost equals marginal revenue
- d. marginal cost equals demand
-
33. All markets that are NOT perfectly competitive have which of
the following
characteristics?
- a. each firm's demand curve is the industry demand
curve
- b. products that the various firms sell are always
differentiated to some extent
- c. firms in the market have some control over price
(face a downward sloping
demand curve)
- d. there are only a few firms in the industry
- e. all the firms make substantial profits
-
34. For price discrimination to be possible between different
buyers, the seller must,
among other things,
- a. prevent resale of the commodity
- b. rely on the ignorance of one consumer about what
other consumers are paying
- c. produce at decreasing cost
- d. face an inelastic demand
-
35. Marginal revenue product (MRP) equals
- a. the product's price times marginal product
- b. the product's price times marginal cost
- c. marginal revenue times the product's price
- d. marginal revenue times marginal product
-
36. The firm's demand curve for an input is downward sloping
because of the
- a. willingness of workers to offer more labor at a
higher price
- b. law of diminishing marginal productivity
- c. fact that most firms buying factors of production
are at least partial
monopolists
- d. fact that unions exist in many labor markets
Use the table below to answer question number
36
| Number of Workers | Wage
Rate |
Marginal Revenue Product |
| 0 |
$4 |
- |
| 1 |
$4 |
$6 |
| 2 |
$4 |
$5 |
| 3 |
$4 |
$4 |
| 4
| $4 |
$3 |
-
37. According to the information in the
table above, the number of
workers that should be hired to
maximize profit is:
- a. 1
- b. 0
- c. 4
- d. 3
-
38. In a perfectly competitive labor
market, the supply curve of labor faced
by the individual firm is
- a. given by the value of the
marginal product (VMP) of labor
curve
- b. the upward sloping portion of the marginal factor
cost (MFC) of labor curve
- c. perfectly inelastic at the market wage
- d. equal to the market wage
-
39. A firm which is the sole employer in a particular area may
be classified as
- a. an oligopolist
- b. a duopolist
- c. a monopolist
- d. a monopsonist
-
40. The wage rate a monopsonist would pay
- a. is less than the marginal revenue product
- b. is equal to the marginal factor cost
- c. is equal to the marginal revenue product
- d. is greater than the marginal revenue product
- e. is greater than the marginal factor cost
 Back to the Final Exam Listings
Back to the Final Exam Listings