Economics 165 Final Exam
Spring
1995
-
1. Economic models or theories
- a. are limited to variables that are directly
(positively) related
- b. are simplifications of the real world they
represent
- c. cannot be tested empirically
- d. are limited to variables that are inversely
related
-
2. Allocative efficiency means that
- a. opportunity cost has been reduced to zero
- b. resources are allocated to the use which has the
highest value to society
- c. technological efficiency has not been achieved
- d. only relative scarcity exists
-
3. Operating inside a society's production possibilities
frontier is a:
- a. drawback of capitalism relative to socialism
- b. symptom of inefficiency or idle resources
- c. way to build reserves to stimulate investment and
growth
- d. result whenever the capital stock depreciates
rapidly
-
4. Which event will shift the butter/guns production
possibilities frontier outward?
- a. a new and superior method of producing butter
- b. a decrease in the resources devoted to the
production of investment goods
- c. an increase in the production of guns
- d. a reduction in the production of butter
-
5. Which of the following is correct with respect to a firm's
supply of a given
product? The supply curve shows
- a. the amount of profit that will be earned for
various output levels
- b. the amount of a good that will be available for
sale at various prices
- c. an inverse relationship between price and
quantity supplied
- d. the amounts of a good that will be sold at
various prices
-
6. If the real income of a consumer decreases and, as a result,
his demand for product
X increases, it can be concluded that product X is a/an
- a. complementary good
- b. normal good
- c. inferior good
- d. substitute good
-
7. If beer and pretzels are complementary goods, then an
increase in the price of beer
will result in:
- a. an increase in the demand for pretzels
- b. an increase in the demand for beer
- c. a decrease in the demand for pretzels
- d. a decrease in the demand for beer
-
8. Excess demand occurs whenever
- a. quantity demanded is less than quantity supplied
- b. goods are scarce
- c. the actual price is greater than the equilibrium
price
- d. the actual price is less than the equilibrium
price
-
9. At the equilibrium price in a market,
- a. there is no tendency for price to change
- b. quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded
- c. there is a tendency for price to rise
- d. there is a tendency for price to fall
- e. quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied
-
10. The price of lettuce rose 70 percent during the 1970's and,
as a result, sales of
salad dressing fell by more than 25 percent. In economic
terms:
- a. the cross elasticity of demand is negative
indicating the two goods are
substitutes
- b. the price elasticity of supply for salad dressing
is low
- c. salad dressing has low price elasticity of demand
- d. the cross elasticity of demand is negative
indicating these are complementary
goods
-
11. Which of the following is not a determinant of the price
elasticity of demand?
- a. the price elasticity of supply
- b. whether the product is a necessity
- c. whether the product is a luxury
- d. the time period in question
-
12. The law of diminishing marginal utility:
- a. provides an explanation for perfectly elastic
demand curves
- b. suggests that as a individual's consumption of a
good increases, his marginal
utility must eventually decrease
- c. suggests that total utility will eventually
decrease if enough of the good
is consumed
- d. suggests that as a consumer buys more of a good,
its price will drop
-
13. To maximize total utility, consumption should be arranged
such that the
- a. the total utility associated with each good
consumed is equal for all goods
consumed
- b. the ratio of the total utility associated with
each good consumed to the
price of the good is equal for all goods consumed
- c. marginal utility associated with the last unit of
each good consumed is equal
for all goods consumed
- d. ratio of the marginal utility associated with the
last unit of each good
consumed to the price of the good is equal for all
goods consumed
-
14. Which of the following will generate additional American
demand for the Mexican
peso?
- a. increased American travel to Mexico
- b. decision by Mexican petroleum companies to invest
in the American oil fields
- c. new American tariffs levied against Mexican goods
- d. decline in American demand for tequila produced
in Mexico
-
15. Quotas tend to be associated with efforts to:
- a. expand domestic production
- b. raise foreign consumer prices
- c. lower domestic consumer prices
- d. lower profits in domestic industries
-
16. An example of an implicit cost is the
- a. interest that a corporation could earn on its
undistributed profits
- b. salaries paid to the managers of the firm
- c. rent paid by a firm for the use of a warehouse
- d. property taxes paid by the firm
- e. wages paid to the blue collar worker
-
17. A driver wishes to buy gasoline and have his car washed. He
finds that the market
price of gasoline is $1.08 and that the wash costs $1.00
when he buys 19 gallons
but that if he buys 20 gallons, the car wash is free. The
marginal cost of the
twentieth gallon is:
- a. $1.00
- b. zero
- c. 8 cents
- d. $1.08
-
18. When the total product of a resource is at a maximum then:
- a. average product is equal to marginal product
- b. average product is equal to zero
- c. marginal product is equal to zero
- d. average product is at its maximum
- e. marginal product is at its maximum
-
19. Which of the following is true concerning short-run total
costs?
- a. total costs are minimized when average total
costs are minimized
- b. total costs are at a maximum when the average
physical product of labor is
at its maximum value
- c. at zero output, total costs equal zero
- d. total costs equal total variable costs plus total
fixed costs
-
20. The long-run average cost curve
- a. suggests that firms always utilize their fixed
plant and capacity in an
efficient manner
- b. suggests that firms will build over-sized plants
and underutilize them at all
levels of output
- c. is the sum of the short-run average-cost curves
facing a firm
- d. indicates the lowest average costs associated with
different levels of output
-
21. If a perfectly competitive firm sells 250 units of output at
a market price of 55
dollars per unit, its marginal revenue is:
- a. $55
- b. $110
- c. more than $55 but less than $13,750
- d. less than $55
-
22. In a perfectly competitive market, the demand curve facing
the firm is
- a. negatively sloped regardless of the
characteristics of the market demand
curve
- b. perfectly elastic while the market demand curve is
typically negatively
sloped
- c. identical to the market demand curve
- d. perfectly inelastic even though the market demand
curve is not
-
23. If the marginal cost of a firm is rising and greater than
its marginal revenue, the
firm should
- a. shut down in the short run
- b. shut down in the long run
- c. increase output to increase revenue and profit
- d. remain at the same level of output since any
change would lead to larger
losses
- e. decrease output
-
24. The perfectly competitive firm's supply curve is exactly the
same as:
- a. its marginal cost curve for all prices above
average variable cost
- b. its fully allocated costs
- c. the supply curve of all firms in the economy
- d. its average variable cost curve
-
25. When a perfectly competitive firm is in long-run
equilibrium, the market price is
equal to:
- a. average total cost, but may be greater or less
than marginal cost
- b. marginal revenue, but may be greater or less than
both average and marginal
cost
- c. marginal cost, but may be greater or less than
average cost
- d. average total cost and also to marginal cost
-
26. Assuming no externalities, perfect competition results in
efficient resource
allocation (allocative efficiency) because price:
- a. is greater than average variable cost
- b. is equal to marginal cost
- c. equals average total cost
- d. is less than marginal cost
- e. is equal to long-run average cost
-
27. The monopolist's demand curve is
- a. identical with the industry or market demand curve
- b. nonexistent
- c. perfectly elastic
- d. perfectly inelastic
-
28. To maximize profits, a monopolist should produce at that
level of output at which:
- a. demand and marginal cost intersect
- b. demand and average cost intersect
- c. marginal revenue equals marginal cost
- d. marginal revenue equals average total cost
- e. average total cost and marginal cost
intersect
-
29. Which of the following may be a benefit to society
associated with monopolistic
competition that does not exist with perfect competition?
- a. homogeneous products
- b. interdependence in decision making
- c. arbitrage
- d. product differentiation
-
30. In long run equilibrium, the typical monopolistically
competitive firm will
- a. earn a positive economic profit
- b. face a perfectly elastic demand curve
- c. earn only a zero economic profit
- d. cease to advertise
- e. no longer need to engage in nonprice
competition
-
31. The number of firms in an oligopoly must be
- a. large enough that firms cannot closely monitor
each other
- b. small enough that firms are interdependent in
decision making
- c. less than a dozen
- d. large enough that firms cannot collude
- e. large enough that firms will see no reason to
engage in nonprice competition
-
32. When a group of individuals or firms who produce and supply
the same good form an
organization whose purpose is to reduce competition between
themselves, the
organization is known as a __________. This group, if
successful, will (raise/ lower/
maintain) the level of output supplied relative to that
produced previous to the
organization's existence.
- a. oligopoly, lower
- b. natural monopoly, raise
- c. cartel, lower
- d. monopoly, lower
-
33. Which of the following is a FALSE statement? Imperfect
competition implies that in
the long run
- a. too little of the good is produced relative to
the societal optimum
- b. the firms demand curve is not horizontal
- c. the firm may not produce at its minimum average
total cost
- d. price may be greater than marginal revenue
- e. price is equal to marginal cost
-
34. Output for a price discriminating monopolist, in comparison
to a single-price
monopoly, will be
- a. lower and profits will be lower
- b. lower and profits will be higher
- c. higher and profits will be lower
- d. higher and profits will be higher
-
35. As labor costs account for a larger portion of total costs,
demand for labor becomes
- a. perfectly elastic
- b. perfectly inelastic
- c. less elastic
- d. more elastic
-
36. The demand for labor is
- a. likely to increase with decreases in resource
price
- b. a direct relationship between resource price and
quantity demanded
- c. a derived demand
- d. always unitary elastic
- e. an inverse relationship between quantity
available and quantity demanded
-
37. Consider a situation in which there is perfect competition
in both the input and
output markets. The firm will hire that input level which
equates
- a. marginal revenue product with marginal factor cost
- b. marginal physical product with marginal factor
cost
- c. marginal factor cost with supply
- d. marginal revenue product with demand
- e. marginal revenue product with marginal physical
product
-
38. In a perfectly competitive labor market, the supply curve of
labor faced by the
individual firm is
- a. given by the value of the marginal product (VMP)
of labor curve
- b. the upward sloping portion of the marginal factor
cost (MFC) of labor curve
- c. perfectly inelastic at the market wage
- d. equal to the market wage
-
39. In a nonunionized monopsonistic labor market the wage rate
- a. will be higher and the level of employment lower
than in a competitive labor
market
- b. will be lower and the level of employment higher
than in a competitive labor
market
- c. and the level of employment will both be higher
than in a competitive labor
market
- d. and level of employment will both be lower than in
a competitive labor market
- e. any one of the above is possible
Use the graph below to answer question number
40
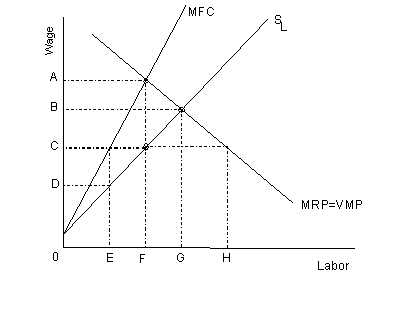
- 40. The firm in the graph above will
pay its workers a wage of $____.
- a. 0-C
- b. 0-D
- c. 0-A
- d. 0-B
 Back to the Final Exam Listings
Back to the Final Exam Listings

