Economics 165 Final Exam
Spring 1998
- 1. The question of HOW production will be organized in a
market economy is most directly determined by:
- * a. suppliers or entrepreneurs
- b. the National Economic Planning Commission
- c. consumers
- d. economic forecasters
- 2. The difference between a scarce (economic) good and a
free good is that
- * a. for free goods at a price of zero enough of the good
is available to completely satisfy consumers' demand for
the good
- b. free goods no longer exist -- there are only scarce
goods
- c. free goods are made with natural resources
- d. free goods are provided by the government
- 3. A reduction in the amount of unemployment
- a. moves the economy along the production possibilities
frontier
- b. moves the economy further away from the production
possibilities frontier
- c. shifts the production-possibilities frontier
- * d. moves the economy closer to the production
possibilities frontier
- 4. A production possibilities frontier will shift out
when:
- a. the production of investment goods decreases
- * b. the quantity and/or productivity of resources
(factors of production) increases
- c. unemployment is decreased
- d. the labor force decreases
- 5. The typical demand curve is
- a. vertical
- b. horizontal
- c. positively sloped
- * d. negatively sloped
- 6. Suppose the law prohibiting possession of
marijuana in quantities of less than one ounce were
abolished and at the same time penalties for the production
or sale of marijuana were increased. As a result
of these two changes, the demand for marijuana would
(increase/decrease) and the supply of marijuana would
(increase/decrease), the price of marijuana then should
(rise/fall/neither rise nor fall).
- a. decrease, decrease, neither
- b. decrease, increase, fall
- * c. increase, decrease, rise
- d. increase, decrease, neither
- 7. If the demand for product J shifts to the left as the
price of product K increases, then
- * a. J and K are complementary goods
- b. J and K are not related goods
- c. the number of consumers of product K has increased
- d. J and K are substitute goods
- 8. Suppose that as the price of gasoline rises from $1.00
per gallon to $1.50 per gallon, the quantity of gasoline
sold increases from 100 trillion gallons to 150 trillion
gallons. Which of the following is a possible explanation
for this?
- a. There were fewer users of automobiles
- * b. The price of public transportation increased over
the same time period
- c. The demand curve for gasoline is perfectly inelastic
- d. All of the above are possible explanations
- 9. Price elasticity of supply is the
- a. change in quantity supplied due to a change in
quantity demanded
- * b. percentage change in quantity supplied divided by
the percentage change in price
- c. responsiveness of supply to changes in costs
- d. responsiveness of the price to changes in supply
Use the graph below to answer question
number 10
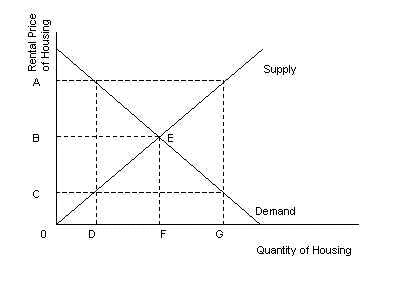
- 10. If a price ceiling is imposed on the rental price of
housing (assume the government can enforce the price
ceiling) then:
- * a. a ceiling price of OC will result in a shortage of
DG units of housing
- b. a ceiling price of OA will result in a shortage of DG
units of housing
- c. a ceiling price of OC will result in a surplus of DG
units of housing
- d. a ceiling price of OA will result in a surplus of DG
units of housing
- 11. Suppose the price of a certain good fell from $1 to
$.50 and the quantity demanded increased from 250 to 750
units. Over this range of the demand curve, the
elasticity of demand is:
- a. 1
- b. .75
- * c. 1.5
- d. 1.2
- 12. The price that one is willing to pay for a unit of a
good depends on its
- * a. marginal utility
- b. cost of production
- c. total utility
- d. supply
- 13. Utility refers to the
- * a. satisfaction derived from consuming a good or
service
- b. net social benefit of a good or service
- c. market value of a good or service
- d. scarcity price of a good or service
- 14. When U.S. residents demand German marks:
- a. they plan to spend those marks on American produced
goods
- b. they can only use those marks to purchase gold from
the German Central Bank
- * c. U.S. residents at the same time supply dollars to
German residents
- d. U.S. residents at the same time demand U.S. dollars
from German residents
- 15. Which of the following could NOT result from a
tariff?
- * a. consumers to be better off because there are more
goods available
- b. consumers to be worse off because there are fewer
imports
- c. domestic producers to be better off because they sell
more goods
- d. domestic producers to be better off because they sell
at a higher price
Use the Table below to answer question
number 16
- Output
|
- Total Cost
|
- 0
|
- $24
|
- 1
|
- $33
|
- 2
|
- $41
|
- 3
|
- $48
|
- 4
|
- $54
|
- 5
|
- $61
|
- 6
|
- $69
|
- 16. In the table above, the total variable cost of
producing 5 units is:
- * a. $37
- b. $24
- c. $61
- d. $48
- 17. Explicit costs differ from implicit costs in that
explicit costs are:
- * a. paid to others whereas implicit costs do not
represent a payment to others
- b. true costs; implicit costs are not part of total
economic costs
- c. not deductible for tax purposes
- d. not necessarily paid whereas implicit costs are always
directly paid
- Use the table below to answer question number 18
- Units of Labor per Day
|
- Total Units of Output per Day
|
- Total Fixed Costs per Day
|
- 0
|
- 0
|
- $120
|
- 1
|
- 10
|
- $120
|
- 2
|
- 30
|
- $120
|
- 3
|
- 60
|
- $120
|
- 4
|
- 100
|
- $120
|
- 5
|
- 120
|
- $120
|
- 6
|
- 126
|
- $120
|
- 7
|
- 119
|
- $120
|
- 18. In the table above, the average fixed cost associated
with an output of 100 units per day is _________ ?
- a. $30.01
- * b. $1.20
- c. $120
- d. $0
- 19. If marginal cost lies below average total cost, then
- a. average fixed cost must be rising
- b. average total cost must be rising
- * c. average total cost must be falling
- d. marginal cost must be falling
- e. marginal cost must be rising
- 20. The marginal product of capital divided by its price
is half as large as the marginal product of labor divided
by its price. For production costs to be minimized:
- a. more capital should be used and less labor
- * b. more labor should be used and less capital
- c. the price of capital must fall
- d. the firm must increase production to reach the minimum
point of the short-run average cost curve
- 21. The demand curve of a perfectly competitive firm
- a. is the same as the market demand curve for the entire
industry
- * b. is perfectly elastic
- c. has a price elasticity coefficient of less than 1
- d. is perfectly inelastic
- 22. A perfectly competitive firm
- a. is likely to earn positive economic profit in the long
run
- b. will always exit the industry if it is incurring
losses in the short run
- * c. is a price taker
- d. always produces at the minimum average total cost
- 23. At the output where a firm's average total cost
equals its price, the firm is
- a. incurring an economic loss
- b. earning more than a break-even return
- c. earning an economic or pure profit
- * d. earning zero economic profits
- e. earning less than a break-even return
- 24. Where marginal cost is rising and exceeds marginal
revenue, a profit-maximizing firm would
- a. continue producing the same level of output in the
short run
- b. shut down in the long run
- c. produce more
- * d. produce less
- 25. A decrease in demand that results in economic losses
in a perfectly competitive industry will:
- a. encourage entry into the industry
- * b. encourage exit from the industry
- c. induce new, more efficient, firms to enter the
industry
- d. cause existing firms in the industry to expand the
scale of their operation
- 26. If entry of new firms into a perfectly competitive
market results in higher resource costs, the long-run
market-supply curve will be
- a. negatively sloped
- b. perfectly inelastic
- c. perfectly elastic
- * d. positively sloped
- 27. Monopolists
- a. are guaranteed at least a zero economic profit
- b. are guaranteed more than a normal profit
- c. are guaranteed an economic profit
- * d. none of the above are correct
- 28. For the monopolist, at the profit maximizing level of
output in the short run, all of the following necessarily
hold except
- a. Price is greater than MC
- b. ATC is greater than Average Variable Cost (AVC)
- * c. Marginal Cost (MC) equals Average Total Cost (ATC)
- d. Marginal Revenue (MR) equals MC
- 29. In monopolistic competition there are
- a. many firms each producing a homogeneous product
- b. a few firms each producing a differentiated product
- * c. many firms each producing a differentiated product
- d. a few firms each producing a homogeneous product
- 30. If additional firms enter a monopolistically
competitive industry
- a. the price would most likely increase
- * b. the demand facing an existing firm would decrease
- c. the demand facing an existing firm would increase
- d. the profits of an existing firm would increase
- 31. In oligopoly markets there
- a. is a single source of supply
- b. is a single source of demand
- c. are a large number of firms each selling a homogeneous
product
- d. are a large number of firms each selling a highly
differentiated product
- * e. is a small number of firms each selling either a
differentiated or a homogenous product
- 32. "Mutual Interdependence" means that
- a. each firm in the market makes homogeneous products
- * b. a single firm will consider reactions of rivals to
any action the single firm takes
- c. pricing actions of rivals in the market are of no
consequence to a single firm
- d. each firm in the market makes differentiated products
- e. the demand curves of the firm and the market are
identical
- 33. All markets that are not perfectly competitive
have which of the following characteristics?
- a. each firm's demand curve is the industry demand curve
- b. products that the various firms sell are always
differentiated to some extent
- * c. firms in the market have some control over price
(face a downward sloping demand curve)
- d. there are only a few firms in the industry
- e. all the firms make substantial profits
- 34. If a firm which is unable to price discriminate is
faced with a downward sloping demand curve:
- a. its supply curve is its marginal cost curve above its
average variable cost curve
- * b. its marginal revenue curve is less than its price
- c. its marginal revenue curve equals its price
- d. its most profitable output is where marginal cost
equals price
- 35. The price elasticity of demand for labor will be
greater
- a. the more difficulty it is to substitute capital for
labor
- b. the smaller is the proportion of total costs accounted
for by labor
- * c. the greater is the price elasticity of demand for
the output
- d. the shorter is the time period for adjustment
- 36. An increase in the market demand for labor will
cause:
- a. the supply of labor to rise
- * b. the wage rate to rise and the quantity of labor
employed to rise
- c. the level of employment to fall
- d. the wage rate to fall
- 37. A firm which is perfectly competitive in both its
output and labor market should hire an additional worker
if
- a. marginal product would be decreased
- b. marginal product would be increased
- c. total revenue is less than total cost
- d. marginal revenue product is less than the wage rate
- * e. marginal revenue product is more than the wage rate
- 38. If both the output and the labor market are perfectly
competitive, the wage will be
- * a. about equal to the value of the additional output
produced by the last worker hired
- b. mainly determined by the bargaining power of unions
- c. driven down to the subsistence level
- d. about equal to the value of the average product of
labor
- 39. A monopsonist, as compared to a perfect competitor in
the labor market, would
- a. pay the same wage and employ more labor
- b. pay the same wage and employ less labor
- c. pay a higher wage and employ more labor
- d. pay a higher wage and employ less labor
- * e. pay a lower wage and employ less labor
- 40. A monopsonistic firm will pay a wage that is
- a. greater than the marginal factor cost
- b. equal to the opportunity cost of the employer
- * c. less than the marginal factor cost
- d. equal to the marginal factor cost
- e. equal to the cost of capital

Back to the Final Exam Listings


![]()